Când am apărut noi, oamenii?
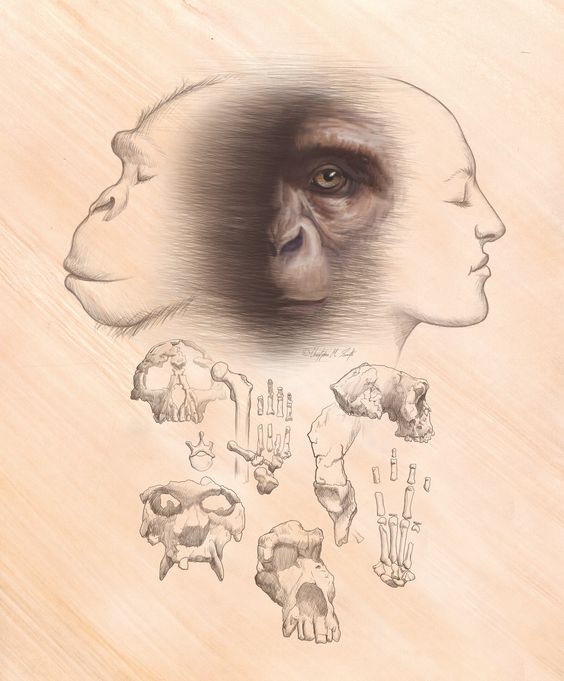
Cu pasul meu ezitant, am pornit într-o călătorie înapoi în timp, în lumea strămoșilor noștri, către momentul în care noi, oamenii, am apărut pe Terra. Această călătorie ne duce cu milioane de ani în urmă, În Africa, locul în care povestea noastră începe.
În urmă cu aproximativ 7 milioane de ani, în Africa, au apărut primii hominizi, strămoșii noștri îndepărtați. Aceste creaturi primordiale au reprezentat primii pași ai evoluției umane. Din această ramură a arborelui genealogic al viețuitoarelor, a apărut genul Homo, o etapă crucială în drumul către noi, Homo sapiens.
Cu trecerea milioanelor de ani, Homo sapiens au luat ființă în Africa de Est, acum aproximativ 200.000 de ani. Prin fosile și artefacte descoperite în Valea Rift din Kenya și Tanzania, cercetătorii au obținut indicii prețioase despre aceste prime populații umane. Erau vânători-culegători, cu tehnologie rudimentară, dar cu potențial imens.
O dată cu evoluția noastră, am început să explorăm și să colonizăm tot mai multe teorii, migrând pe tot globul. Abilitățile noastre cognitive, dezvoltarea limbajului și capacitatea de a crea unelte au fost cheile adaptabilității noastre. Ne-am răspândit în Asia, Europa, Australia și America, dezvoltând culturi și societăți diverse.
Genetica a adus o altă dimensiune în înțelegerea originii noastre. Studiile genetice au dezvăluit că toți oamenii moderni au un strămoș comun în Africa de Est. ADN-ul nostru păstrează amprenta migrației noastre și a relațiilor dintre populații. “Eva mitocondrială”. strămoașa comuna a tuturor ființelor umane, a trăit aproximativ 200.000 de ani.
Acesta este dor începutul poveștii noastre. Evoluția umană nu s-a oprit odată cu apariția noastră că Homo sapiens. Descoperirile și cercetările continue aduc mereu lumini noi în istoria noastră. În cele din urmă, ne ajută să înțelegem mai bine originile noastre și complexitatea călătoriei umane pe Pământ.Ceea ce știm acum reprezintă doar un punct de pornire într-o explorare continuă a trecutului nostru fascinant.
English Version:
When did humans first appear?
With my hesitant steps, I embarked on a journey back in time to the world of our ancestors, to the moment when we, humans, first appeared on Earth. This journey takes us millions of years ago to Africa, where our story begins.
About 7 million years ago, the first hominids, our distant ancestors, appeared in Africa. These early creatures marked the first steps in human evolution. From this branch of the family tree of living beings, the genus Homo emerged, a crucial stage in our path to becoming Homo sapiens.
Over the course of millions of years, Homo sapiens came into existence in East Africa, approximately 200,000 years ago. Through fossils and artifacts found in the Rift Valley of Kenya and Tanzania, researchers gained valuable insights into these early human populations. They were hunter-gatherers with rudimentary technology but tremendous potential.
As we evolved, we began to explore and colonize more and more regions, migrating across the globe. Our cognitive abilities, the development of language, and our tool-making skills were key to our adaptability. We spread to Asia, Europe, Australia, and the Americas, developing diverse cultures and societies.
Genetics added another dimension to understanding our origins. Genetic studies revealed that all modern humans share a common ancestor in East Africa. Our DNA retains the footprint of our migrations and relationships between populations. “Mitochondrial Eve,” the common ancestor of all human beings, lived approximately 200,000 years ago.
This is just the beginning of our story. Human evolution didn’t stop with the appearance of Homo sapiens. Ongoing discoveries and research continually shed new light on our history, helping us better understand our origins and the complexity of the human journey on Earth. What we know now is just the starting point in our ongoing exploration of our fascinating past.




